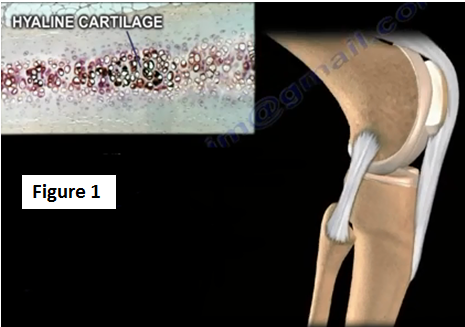
The cartilage of the knee is complex and it is made up of an elastic compressive structure. The normal articular cartilage is called hyaline cartilage. Hyaline cartilage provides a smooth, gliding surface that helps in the motion of the joint (Figure 1).
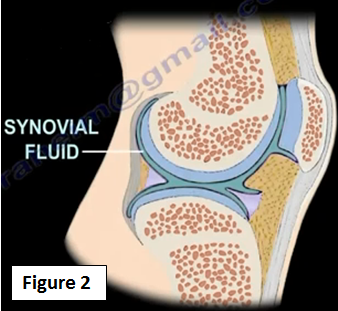
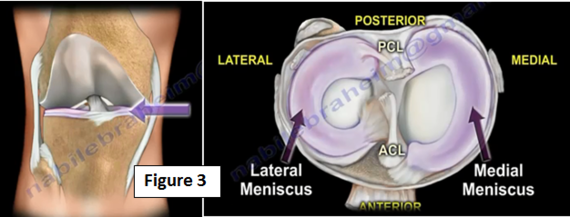
There is about 2 cc's of synovial fluid inside the knee which helps in the motion and lubrication of the joint (Figure 2). Between the hyaline cartilage (articular cartilage) is the meniscus. The meniscus is a shock absorbing cartilage or cushion between the articular cartilage (Figure 3).
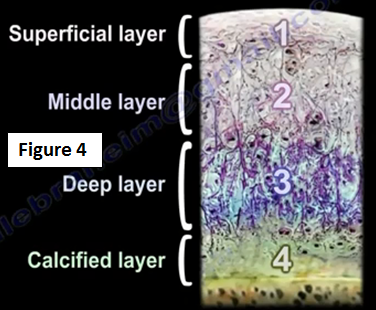
The hyaline cartilage has four layers: superficial layer, middle layer, deep layer, and calcified layer. After the calcified layer is the bone (Figure 4). These cartilage cells are supposed to live forever! Good cartilage cells are sterile and cannot make more cartilage if these cartilage cells are destroyed.
If the cartilage is subjected to excessive wear, excessive trauma or injury, overuse, excessive weight or improper alignment, then the cartilage will wear away leaving the bone to rub against the bone.
If injured, cartilage does not have the ability to heal itself with hyaline cartilage, however it does sometimes heal itself with an inferior type of cartilage called fibrocartilage, especially if the area that needs to be repaired is small.
What is the treatment of arthritis of the knee?
There are a number of treatment options that will help the patient.
1. The doctor will choose the right kind of medication
People respond differently to medications. The doctor usually selects the type, dose and duration of the treatment. The medication has to be safe and effective! In general, all medications have side effects, make sure to ask the doctor questions about any side effects of the prescribed medication.
The selection of medication is usually based on the physician's experience, preference and the patient's susceptibility. The duration of use will be based on the effectiveness, the side effects of the medication and the medical history of the patient. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) will be used (Figure 5). This medication may have side effects. The physician will ask if the patient has gastritis or stomach issues. NSAIDs may cause renal failure or renal issues. The medication may also interfere with fracture healing. COX-2 inhibitors such as Celebrex and Mobic (Meloxicam) can cause less gastrointestinal side effects but may cause other side effects.
Ultram (tramadol) is used for symptomatic osteoarthritis. Some doctors prefer a combination of Ultram (tramadol) and Tylenol (acetaminophen). Medications are a core initial treatment that is very important and recommended.
2. Losing weight
The normal Body Mass Index (BMI) is between 18.5 and 24.9. For a person to be classified as overweight, they would have a BMI between 25 and 29.9. An obese person would be described as someone who has a BMI of 30 or more. If a person's BMI is above 25, diet control and exercise is recommended in order to lose about 5% of the body weight. The patient should be given a nutritional consult and some encouragement.
How to handle a person with metabolic syndrome?
These patients will have abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, elevated fasting blood glucose levels, and dyslipidemia (Figure 6). This is complex patient management and an orthopaedic surgeon will need support from multiple medical consultants.
3. Low impact physical therapy
Low impact activities such as swimming or cycling are usually better and put less stress on the knees (Figure 7). Jogging, running and tennis are high impact activities and will put more stress on the knees. Lifestyle modifications to protect the knee will slow the progression of the arthritis. There is strong evidence that physical therapy will help the patient! Physical therapy will decrease the pain, improve the function of the knee, and increase the strength, range of motion and flexibility of the knee. Physical therapy should be individualized with a program that meets the patient's needs, lifestyle and expectations. The patient should continue physical therapy exercises even if they begin to feel better since the benefit could be lost if the patient stops doing the exercises.
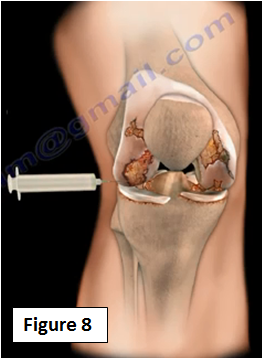
In general, there are a number of treatment options that may help the patient. The initial treatment for arthritis of the knee is usually nonsurgical. The physician will also use intra-articular injection of steroids viscosupplementation, or hyaluronic acid (Figure 8). The injection will relieve the patient's pain and disability. Steroid injections can be administered about 3 - 4 times per year. Viscosupplementation will improve the quality of the joint fluid. The problem with hyaluronic acid and viscosupplementation is the studies that are published do not meet the minimal clinically important improvement threshold.
There clearly is a group of patients which these injections could help. The industry should be encouraged to identify which group of patients will receive the benefits of hyaluronic acid or viscosupplementation injection. Other methods of injection are gene therapy, PRP, growth factors and stem cells. It is logical to pursue the efficacy of stem cells in cartilage regeneration. More clinical trials and more research are needed in this area.
Assistance devices may be helpful. These devices include a cane, shock absorbing shoes, shoe inserts, knee sleeves, and a support brace.
Arthroscopy should not be done with arthritis unless there is a loose body or meniscal tear causing mechanical symptoms of recurring locking, catching, swelling and pain.
Other treatment options with no clinical effective response include acupuncture, massage, glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, valgus directing brace, wedges in the foot, and Arthroscopic Debridement and Lavage.
The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) guidelines are suggestions and treatment options for the patient with arthritis which should be individualized based on the doctor's clinical judgment, the patient's clinical situation and benefit, and the evidence tested and published. The doctor will use a combination of all of these factors to guide the best possible treatment for the patient. What may work for you may not work for your neighbor.
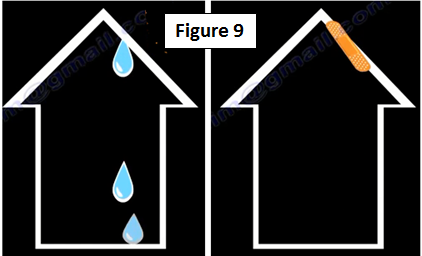
Arthritis of the knee could be minimal and anything could help the arthritis in this situation. Arthritis of the knee is similar to a leaky roof, when you patch it up the leak will stop (Figure 9).
If the knee arthritis is moderate, then the physician has many options for treatment and none of these options have predictable in the result.
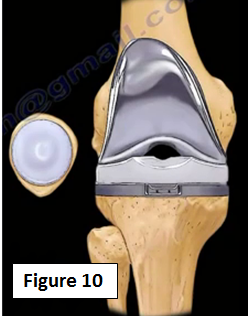
When arthritis of the knee is considered a severe case, simply "patching" the problem will not work. With severe arthritis, a total knee replacement is the most reliable option for treatment (Figure 10).
We need to reduce the level of pain and improve the function of the knee. When the roof of the house is totally destroyed, we have to change the roof, and the same principle applies with a total knee replacement. As arthritis destroys the cartilage of the knee, the water content will increase early, collagen becomes disorganized, protoglycan concentration and synthesis will decrease, and the modulus of elasticity of the cartilage is reduced; a total knee replacement is needed!
The doctor will remove all of the damaged cartilage and bone to insert a new knee. There is some potential risk of complications with every surgery!
Blood clots, infection, pain, failure of the procedure and instability are examples of the complications. the patient is usually given a blood thinner, which may have its own significant complications hemorrhage, hematoma, infection or blood clots. No treatment is waterproof.
There is not a cure for arthritis, injection may help; however, this is only temporary.
For more information on knee pain, follow the links below:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=imRQX5RI0-U
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UJB4eh-Vtz8
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FMXAJhtM1ZA
For more videos, visit my YouTube Channel:
https://www.youtube.com/user/nabilebraheim