
Flames erupted from an offshore drilling rig in the Gulf of Mexico Tuesday night, torching a natural gas plume that had been leaking since a blowout earlier in the day. All 44 rig workers were evacuated before the fire began, according to the U.S. Bureau of Safety and Environmental Enforcement, but the rig continued spewing gas until Thursday morning, when its scorched frame finally collapsed enough to cut off the leak.
In addition to the cloud of natural gas rising from the rig, the BSEE had observed a light sheen on the water's surface measuring half a mile by 50 feet. The well's owner, Walter Oil & Gas, was reportedly making preparations to drill a relief well before the rig "bridged over," clogging the well with sand and sediment. The Associated Press reported Thursday afternoon that the fire is out, the rig appears stable and no sheen is visible.
Located 55 miles off the Louisiana coast, the well's unmanned platform wasn't producing gas when the blowout occured. The 44 workers were on an adjacent, portable rig that was drilling a "sidetrack well" into the original well bore. It's unclear what ignited the gas, the BSEE says, and a diagnosis will likely be delayed by response and cleanup efforts.
"BSEE's efforts today are focused on bringing this loss of well control event to a safe resolution," says Lars Herbst, BSEE Gulf of Mexico regional director, in a statement issued Tuesday. "Offshore oil and gas operators need to re-affirm their aggressive approach to the safety of well operations in light of this event and other recent well control events."
The most salient such event in recent memory is the 2010 Deepwater Horizon disaster, which killed 11 people and released 200 million gallons of crude oil into the Gulf. Officials say there's little chance this week's blowout will come anywhere close to matching that level of devastation, but it does cast a new spotlight on a long-running risk looming off the U.S. Gulf Coast. Earlier this month, for example, another inactive gas well ruptured off the Louisiana coast, leaking a small amount of gas and liquid before it was plugged.
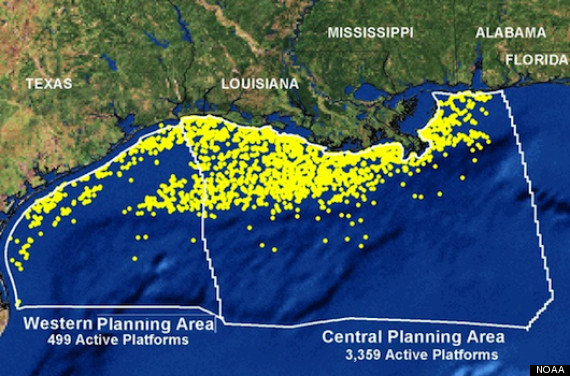
The Gulf of Mexico is dotted with nearly 4,000 active oil and gas platforms (pictured above), plus a sprawling array of drilling rigs, supply ships and pipelines. This seafaring infrastructure is key to a bustling energy sector across the Gulf Coast, especially in Louisiana and Texas, but it also poses a grave danger to nearby people and wildlife.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the U.S. oil and gas extraction industry had a death rate of 27.1 per 100,000 workers between 2003 and 2010. That's seven times higher than the 3.8 deaths per 100,000 workers across all U.S. industries. "The 11 lives lost in the 2010 Deepwater Horizon explosion provide a reminder of the hazards involved in offshore drilling," the CDC report stated.
Beyond the threat from active wells and drilling, the Gulf is also haunted by more than 27,000 abandoned oil and gas wells, most of which undergo no monitoring for leaks. Some of the region's oldest wells were abandoned in the 1940s, and many others are only considered "temporarily abandoned," thus facing less strict sealing requirements.
These wells could be seeping oil, methane or other toxic substances for years, potentially sickening already-threatened wildlife like sea turtles or cetaceans. And as researchers have learned since 2010, large amounts of oil and gas can wreak havoc with microbial life and coral colonies, both of which are key to the Gulf's food web — including its lucrative seafood industry. Although the Gulf is home to microbes that evolved to feed on natural oil and gas seeps, too much unnatural leaking and spilling can smother them.
"It's important to keep in mind that if you keep pumping hydrocarbons into the system, you'll eventually overwhelm it," University of Georgia marine scientist Samantha Joye told MNN earlier this year, referring to the 2010 spill on its three-year anniversary.
Closer to shore, oil and gas development has already transformed many Gulf Coast wetlands, as manmade canals and other extraction-related projects have disrupted the flow of water and sediments that gradually build coastal bayous. The region has lost about 1,900 square miles of land in the past 80 years, and Louisiana alone is projected to lose another 1,750 square miles by 2060. Not only do these marshes house important wildlife, but they also serve as a protective buffer against hurricanes.
Recognizing this risk, Louisiana officials filed a lawsuit Wednesday against dozens of energy companies, seeking damages for decades of harm to coastal wetlands. Filed coincidentally as a leaking gas rig burned offshore, the suit cites "a mercilessly efficient, continuously expanding system of ecological destruction," according to the New York Times, and hints at evolving attitudes in a region that has prospered from drilling but also suffered from lost tourism and seafood income after the Deepwater Horizon spill.
"Coastal economies, which depend on healthy oceans, simply cannot afford more offshore drilling disasters," says Jacqueline Savitz, deputy vice president for the environmental group Oceana, in a statement released Wednesday about the latest gas blowout. "This is yet another reminder that offshore drilling remains dirty and dangerous."
Editor's Note: This post has been updated since it was first published on July 24, 2013.
