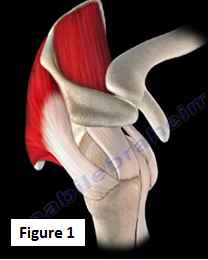
The shoulder joint is the most commonly dislocated joint in the body (Figure 1). The shoulder can be dislocated anteriorly (in front) or posteriorly (in back).
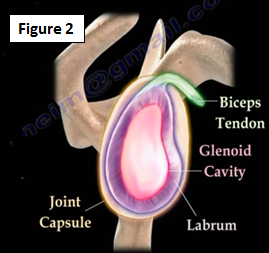
For the purpose of shoulder stability, the labrum acts like a bumper within the joint capsule of the shoulder joint (Figure 2).
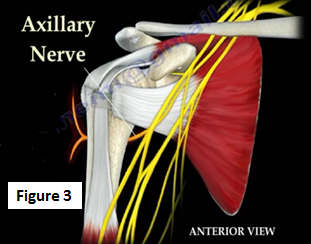
The axillary nerve is most commonly involved in injuries associated with the shoulder joint. It arises from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus and supplies the teres minor and deltoid muscles as well as the skin of the shoulder (Figure 3). Injury to the axillary nerve will result in numbness in the shoulder area and weakness of shoulder abduction.
Anterior Dislocation
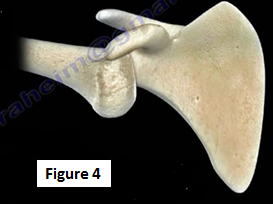
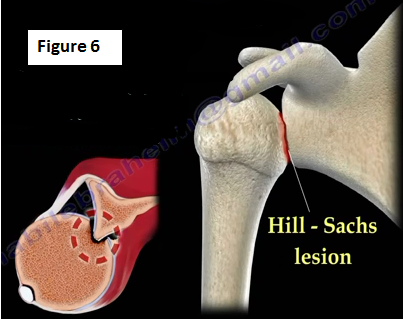
Anterior dislocation is seen in more than 95% of cases involving shoulder dislocation. The mechanism of injury related to anterior shoulder dislocation is usually indirect force with a combination of abduction, extension and external rotation that leads to dislocation (Figure 4). It occurs with the arm in a position away from the body, often overhead, with the arm rotated backwards. Anterior dislocation is often found with a combination of labral tear, greater tuberosity fractures or fractures of the humeral head called Hill-Sachs Lesion.
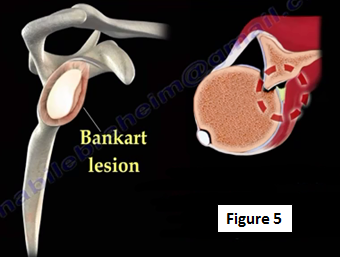
A Bankart lesion refers to a tear of the anterior-inferior labrum of the glenoid rim (Figure 5). Bankart lesions may be associated with a high recurrence rate of dislocation in patients younger than 30 years of age. Bankart lesions can occur either as fibrous or bony. The head of the humerus may impact against the anterior-inferior edge of the glenoid causing a divot or flattening of the humeral head, Hill-Sachs Lesion (Figure 6).
Treatment
The treatment of an anterior dislocation is immediate reduction. A dislocation is ruled out if the patient can touch the opposite shoulder. Immobilization of shoulder dislocations remains a controversial topic in duration and position. Surgery is usually reserved for patients with recurrent instability. The patient is unable to lift the arm after reduction of a shoulder dislocation. If the patient is young, the doctor will need to rule out axillary nerve palsy. In elderly patients, the doctor will have to rule out a cuff tear.
Posterior Dislocation
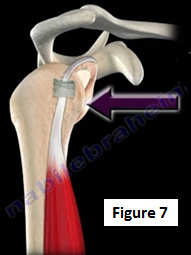
Posterior dislocations are usually associated with seizures or electrical shock and are often missed on radiographs. With posterior shoulder dislocations, there is a lack of external rotation movement at the shoulder joint. Posterior dislocations will dislocate straight posterior, only 5% of shoulder dislocations are posterior (Figure 7). Normal external rotation of the shoulder is possible without the presence of posterior dislocation. The most reliable sign of posterior dislocation is the presence of the shoulder being locked in internal rotation.
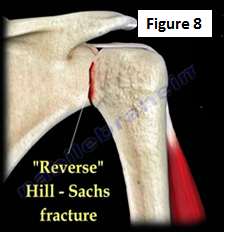
Reverse Bankart lesions, reverse Hill-Sachs fracture or lesser tuberosity fractures of the humeral head may also accompany a posterior dislocation (Figure 8). An axillary radiographic view is used to diagnose posterior shoulder dislocation. The humeral head is seen impacted onto the posterior rim of the glenoid.
Inferior Subluxation of the Shoulder
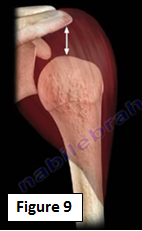
An inferior subluxation of the shoulder is often confused with a shoulder joint dislocation. An axillary radiographic view is normal in these cases. Inferior subluxation is caused by deltoid muscle atony (Figure 9), the muscle of the shoulder has lost its strength to maintain the position of the humeral head within the joint. Treatment is given by physical therapy and electrical stimulation, this conditions improves with time.
For more videos about shoulder pain, follow the links below
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CuZPBxaw5yc
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xn-c2goYzLE
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2OermOgYjL4
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XAwTj9ke4J8
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dgAedXjhxHw
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OuI7AjkU-NY
For more videos, visit my YouTube Channel:
https://www.youtube.com/user/nabilebraheim